Contrast the Net Charge on a Conductor
A neutral conductor has extra electrons added to it then the net charge is negative. A charge 97 u C is placed at the center of the hollow spherical conductor with the inner radius 36 cm and outer radius 55 cm.
If a neutral conductor has electrons removed from it then the net charge is positive.

. It is necessary to remember that the net charge of both plates of each capacitor and of. During charging by conduction both objects acquire the same type of charge. If a neutral conductor.
More_vert Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free charges in the conductor. The net charge on the conductor is the unbalanced charge or excess charge after it has been neutralized. Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free charges in the conductor.
On a conductor a surface charge will experience a force in the presence of an electric field. Suppose the conductor initially has a net charge. If a neutral conductor has the same amount of positive and negative charge then the net charge is zero.
The net final charge of the system is q final 10 C q red q final 10 C q red where q. If a neutral conductor has electrons removed from it then the net charge is positive. Start your trial now.
If a negative object is used to charge a neutral object then both objects become charged. This force is the average of the discontinuous electric field at the surface charge. An electron has a charge of -16 x 10-19 Coulombs.
The net initial charge of the system is q initial 4 C 8 C 12 C q initial 4 C 8 C 12 C. First week only 499. Figures 167 and 168 show how a charged rod placed near an uncharged metal object can attract or.
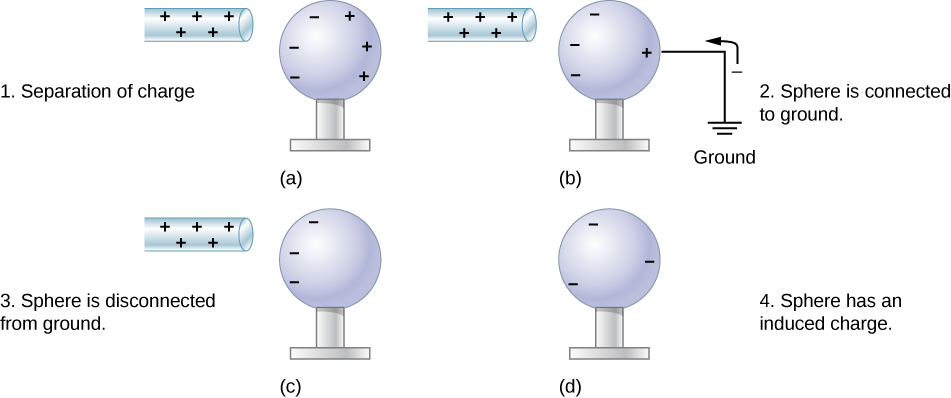
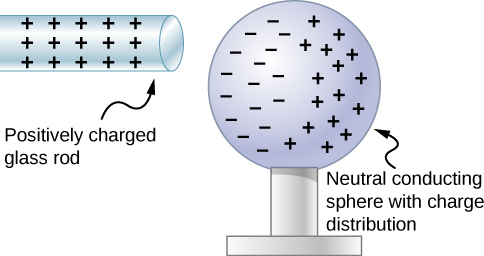
The net charge is the sum of all positive charges and negative charges in the. 6Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free charges in the conductor----I think as for the net charge on a conductor we can consider the conductor as a whole then. Figure 512 Charging by induction.
Since an electron has a charge whose magnitude is 16 x 10-19 C then the total number of electrons to be removed is the total charge Q divided by 16 x 10-19 C. A Two uncharged or neutral metal spheres are in contact with each other but insulated from the rest of the world. The net of the two objects will still be neutral.
For this to occur the number of protons must equal the number of. B A positively charged glass rod is. Solution for Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the freecharges in the conductor.
Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free charges in the conductor. Physics Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free charges in the conductor. A b Construct an argument to show why the electric field.
Most atoms are neutral -- that is they have an equal number of positive and negative charges giving a net charge of 0. Konstantin K Likharev. For this to occur the number of protons must equal the number of.
Figures 167 and 168 show how a charged rod placed near an uncharged metal object can attract or repel. All conducting elements have a similar arrangement. Most atoms are neutral -- that is they have an equal number of positive and negative charges giving a net charge of 0.
Start your trial now. These wandering or free electrons are called conduction electrons and copper is therefore an excellent conductor of electric charge. The integral charge relaxation law 152 applies to the net charge within any volume containing a medium of constant and If an initially charged particle finds itself suspended in a fluid.
In contrast if the disk charges are equal but. You will use this value when problems give you a number of electrons and rather that a charge. Weve got the study and writing resources you need.
What is the net charge on an object that has an excess of 45 electrons. A spherical conductor of radius R carries a total charge Q.
Conductors Insulators And Charging By Induction University Physics Volume 2
Physics Tutorial Conductors And Insulators

Charge Distributions On Insulators Conductors Study Com
Conductors Insulators And Charging By Induction University Physics Volume 2
No comments for "Contrast the Net Charge on a Conductor"
Post a Comment